Whether you’re interested in becoming a professional web developer or you simply want to learn more about how websites work, the first thing you need to study is HTML.
HTML is the standard language that is used for creating webpages and web applications. Every time you access a website, a server sends an HTML file to your computer and your browser interprets and displays the information included in that file. In fact, all the information you are reading now is simply data that has been stored in an HTML file and sent to your browser.
Here’s the best thing about HTML – it’s a simple language to learn.
Most people can learn the basics of HTML in just a few hours, and with a solid HTML foundation, you can progress to more complex languages such as CSS and JavaScript.
This guide will provide an introduction to writing HTML, examine the basic building blocks of HTML such as tags, elements and attributes, and help you create your first HTML page by following a step-by-step tutorial. By the end of this guide, you should have the basic knowledge required to start working on your own HTML projects.
What Is HTML?
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, which can be a confusing term for many beginners. The best way to explain HTML is to examine the meaning of each word.
Hyper Text refers to text that contains links to other texts. Every time you click on a highlighted or underlined link that takes you to another page, you are using hypertext. As more and more pages use hypertext to link to each other, a “web” of pages starts to form. This is where we get the term World Wide Web.
Markup refers to the special symbols or codes that are inserted into a document to tell the web browser how to display the document data. For example, markup code may tell the browser to display a phrase in bold or italic text, or may tell the browser which parts of the document are headings and which are paragraphs. HTML is just one of a number of languages that uses markup code.
Language refers to the idea that the code is standardized. Just like regular spoken languages, there are certain rules that everyone must follow when writing HTML. This is so that all browsers can understand and interpret the code. There are many different programming languages, and you may have heard of some of the popular ones such as Java, Python and Ruby. Each language has its own unique set of rules, and many languages can be used in combination with HTML to create amazing webpages and applications.
If we put these three definitions together, we could say that HTML is “a programming language that uses unique code which allows you to display linked documents in a browser”.
Why Should You Learn HTML?
These days, website builders such as Wix and Site Builder have made building websites easy. With a simple drag and drop interface and a variety of templates, anyone can build a website that is both functional and stylish.
But what if you’re not interested in having a website that looks just like everyone else’s? What happens when you want to make changes to your site that go beyond what’s available using the drag and drop builder?
With a basic knowledge of HTML (as well as a little CSS), you can build a truly unique website that you can edit and update yourself, and you won’t have to pay expensive monthly service fees.
Learning HTML is also considered the first step for progressing into more complex and in-demand programming languages. Fancy earning a six-figure salary as a web developer for a Silicon Valley startup? Or maybe you’ve got plans to develop the next Facebook or Twitter? If you’re interested in learning how to do any web related programming, HTML is the place to start.
Are There Different Versions Of HTML?
The first version of HTML was developed by physicist Tim Berners-Lee in 1990, and the first publicly available version was released in 1991. Since then, HTML has been updated numerous times to address advances in technology.
The current standardized version is HTML5, which has been in use since 2014.
Recommendations for change is HTML are made by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), a standards organization created with the purpose of developing guidelines and protocols for ensuring the long-term growth of the Web.
How Does HTML Relate To Other Programming Languages?
If you’ve done any research on web development and design, you’ve probably come across articles or guides that mention CSS and JavaScript.
HTML, CSS and JavaScript are the three main languages that are used to create most webpages. Each of the languages has a different function and each has different rules, but they all work together to give webpages content, design and functionality.
As we mentioned before, HTML is the foundation of any site. The HTML code contains the site’s basic structure and content, which includes all the text, links, tables, links to images and other such elements.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to define the design of the page, including things like the size of each element and how it looks. With CSS, you can set things like the style of the font you are using, the background color of the page, and the width of the border around elements on the page.
JavaScript is a more complex language that is used to create interactive elements on your page. When you hover your mouse over an image on a website and the image morphs or changes, that’s JavaScript editing your original HTML code. When you click on a product on a shopping website and your shopping cart automatically updates, that’s JavaScript too.
CSS and JavaScript can add design and functionality to a site, but without HTML, you won’t have a site to begin with. In fact, most sites will still display HTML data even if the CSS and JavaScript code is broken.
Here’s what the Wikipedia HTML page looks like: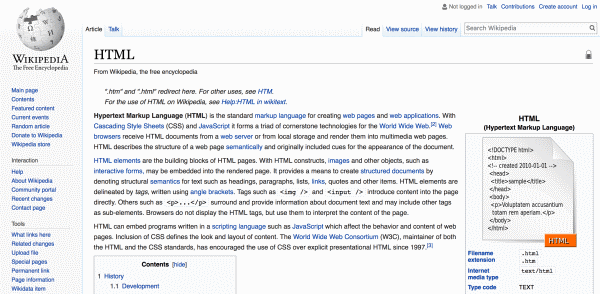
Now here’s what it looks like with CSS and JavaScript disabled:
It doesn’t look pretty, but all the important content is still there.
What Does HTML Code Look Like?
Basically, HTML code looks just like regular text. The most identifiable feature of HTML code is the use of angle brackets. These angle brackets enclose the markup code which tells the browser how to display the document data.
Here’s an example of some simple HTML code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading.</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
If you save this code into a text file with the filename “test.html” and open it in your browser, it should display a page like this:

It’s not very exciting, but it’s a good example of a website in its simplest form. Even without any knowledge of HTML, you can probably understand a little bit about how HTML works by simply looking at the code above and comparing it to the image.
If you’d like to see what a more complex site looks like, try viewing the HTML source code of this page in your browser. The method for viewing source code differs depending on which web browser you’re using.
Microsoft Edge users can click the More icon and select Developer Tools from the drop down menu.
Microsoft Internet Explorer users can click on the View menu and select Source.
Mozilla Firefox users can click on Tools, Web Developer and then Page Source from the menu bar.
Google Chrome users can click on View, Developer and then View Source from the menu bar.
At the moment, the source code of this site probably looks like a foreign language (which is basically what it is), but by the end of this guide you should be able to examine the code again and have a good idea of what is going on.
Good info
ReplyDelete